Can You Put a Plastic Cup in the Microwave? (Microwave Safety Tips)
-
Pete Ortiz
- Last updated:
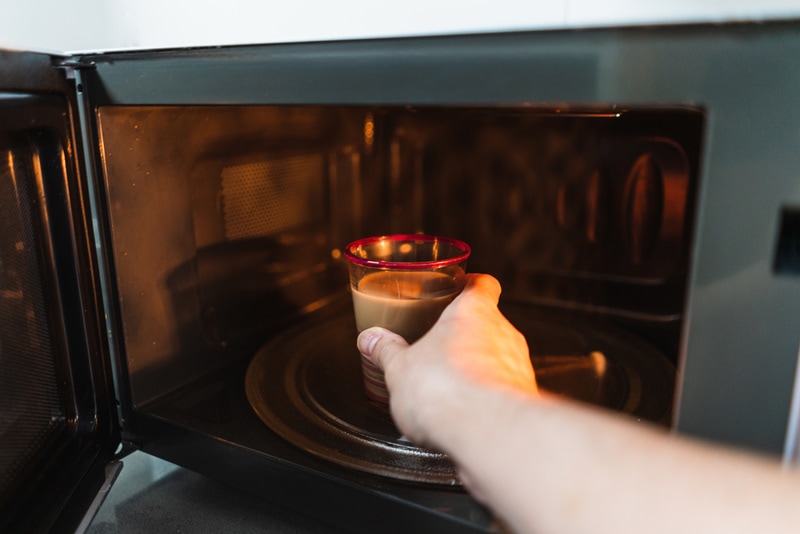

Just like washers and refrigerators, microwaves are a fan-favored household appliance1. They have a permanent place on the kitchen counter and can reheat leftovers, defrost stuff from the fridge, and, of course, cook some food. But what about plastic cups? Can they go into the cooking cavity? To a large extent, no, that’s not recommended because most plastics have a low resistance to heat.
That means they’ll melt, releasing dangerous chemicals like BPA and contaminating the food. That said, there are some cups and plates made of premium-quality plastics that are allowed in the oven. And, as long as they have a “Microwave-friendly” tag at the bottom, they’re safe to use. How do you find them? What are the alternatives? Let’s figure it out!
What Is Plastic? What’s It Made Of?
Plastics are polymers made from crude oil, natural gas, or cellulose2. Salt and coal are also often used to manufacture various plastic products. First, the natural elements are turned into propane or ethane3. Next, these byproducts are turned into plastic through polymerization or poly-condensation. That’s right: most plastics are petroleum-based. They’re not biodegradable, though.
That’s why there are so many bottles, cups, plates, and containers found in landfills across the country. These polymers are not particularly eco-friendly, either. So, why are there so many different plastic types? It all comes down to the monomers used in the manufacturing process. Some plastics are durable and heat resistant. Others are highly flexible and lightweight yet weak against temperature extremes.
BPA and Phthalates: Why Are They Dangerous?
Unfortunately, many plastic containers and cups are dangerous. Primarily, we’re talking about hazardous elements like BPA and Phthalates. These industrial-grade compounds are used in the manufacturing of polycarbonate plastics. And, although we’re all used to storing food in PC containers, they’re not 100% safe. When heated, polycarbonate plastic cups and mugs melt, and the chemicals start to leak.
As a result, your food or drinks get contaminated. The side effects of BPA exposure include diabetes, high blood pressure, and, above all, cardiovascular issues. Phthalates, in turn, are linked to type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, and negative effects on the endocrine system (reproductive issues for men and women). That’s why PC plates or cups are never microwave-safe.

Can Plastic Cups Go Into a Microwave Oven?
Most products made of plastics can’t withstand extreme heat. This is true for children’s toys, automobile parts, Smartphone cases, and, of course, cups. The only time when you can put a plastic cup into the cooking cavity and get away with it is if it’s labeled as microwave-friendly. According to the FDA, food containers with this tag (wavy lines at the bottom) are safe to use and won’t cause any trouble.
It’s important to point out that only a very few brands make plastic cups for microwave use, with the Tervis tumblers leading the charge. The US Food & Drug Administration also recommends sticking to the manufacturer’s instructions on safety, temperature limits, and maintenance. This applies to both the microwave oven and the drink vessels.
Plastic Symbols: What Do They Mean?

Do you use plastic products often? If so, you might’ve noticed that they come with various symbols. Along with the squiggly microwave lines, we have the “Food safe”, “Dishwasher safe”, and “Freezer safe” labels. In addition to that, manufacturers are also required to put recycling information on their products. Here’s a quick look:
- So, #1 stands for PETE (polyethylene terephthalate). This plastic is cheap and easily recyclable but also tends to release chemicals when heated
- HDPE, #2, is high-density polyethylene. It’s the plastic used in milk jugs. HDPE is resistant to heat, yet not always recommended in the microwave
- PVC, AKA polyvinyl chloride (#3), is often used for wrapping food, but it’s highly toxic and not eco-friendly. Only 1% of this plastic is recycled
- Next, we have LDPE, #4, or low-density polyethylene, another easy-to-melt plastic. When exposed to high temps, it deforms and might leach chemicals
- PP, #5, is Polypropylene, the best plastic on the market. It’s durable, heat-resistant, and doesn’t release toxic fumes, which makes it microwave-safe
- And what about PS, short for polystyrene? The #6 plastic is Styrofoam, a lightweight material that leaks styrene when exposed to heat
- Lastly, #7 stands for PC, or polycarbonate—the worst plastic for cooking. As mentioned, PC plastic contains BPA and other hazardous compounds.
Summing up, #5 is the safest plastic to put in a microwave. Plastics #1, #2, and #4 are much worse but can be microwave-safe if they have a label. Plastics #3, #6, and #7 are never safe to use.
Glass and Ceramics: Best Alternatives to Plastics
Don’t want to stress yourself trying to find the safest dinnerware to reheat some leftovers? Then you can go with ceramic. Now, if it’s an old bowl or cup, it might crack when exposed to extreme heat. But, in most cases, it’s the safest material for heating food and drinks. Just make sure you let it sit in the kitchen for a while (at room temperature) if you’ve been keeping it in the freezer.
Skipping this part might also make it crack. And what about glass? Is it stable enough to be microwave-safe? For the most part, yes: glass dishes are almost always safe to go in an oven. This doesn’t mean EVERY single tumbler, mug, or bowl made of glass is 100% safe, of course. So, take a quick look at the label at the bottom. Does it say “Microwave-friendly”? Then you’re good to go!
Should You Use Steel or Paper Cups?
The short answer is no, these materials aren’t safe to go into a microwave. While cups and bags made of paper do a great job of keeping drinks or food warm, they aren’t designed with the oven in mind. Paper isn’t a heat-resistant material—that’s the big issue here. If you keep it in there for a minute or two, that will affect the glue/wax, making the cup leak all over the cooking cavity.
In the worst-case scenario, it will go up in flames, causing a huge headache over a cup of coffee or tea. As for steel, it reflects microwaves instead of absorbing them, which might also make the appliance catch on fire. Sparks will fly, that’s for sure. This is true both for stainless steel and aluminum (especially the aluminum foil that we’re all used to having in the kitchen). If you HAVE to, use thick metal cups or bowls.

Plastics and Microwaves: A Safety Guide
The FDA is very strict when it comes to rating plates, cups, and mugs. That’s what makes the labeling system so reliable. But what if you can’t find any info on whether the product is microwave-friendly or not? Should you just fire up the appliance and go with it, or maybe it would be best to put the crockery to the side? Well, how about a quick test? Here’s what you need to do:
- Put an empty plastic cup of your choosing inside the microwave
- Put another container inside the cooking cavity but this time, fill it with one cup of water
- Set the microwave to “high” and run it for a minute
- Remove the empty container and swiftly check its temperature
- Is it nice and cool? Then you can use it for heating drinks
- If it’s a bit warm, only use it for reheating yesterday’s leftovers
- And if the cup is really hot, keep it as far from the microwave as possible
What Else Should You Do?
Even if the plastic cup is 100% safe to go in a microwave, there are still some things to check. First, never put any container into the oven if it has cracks here and there. The reason: your food or drinks will be quick to spill out. And if it’s not plastic #5, you may also end up with chemicals leaking into the meal. Even the tiniest cracks can cause this—keep that in mind.
Next, when using airtight plastic containers, you need to let them “breathe”. For storage, these containers are great because they keep the food fresh for a long time. However, when exposed to heat, they might crack, which, again, allows the hazardous compounds to contaminate whatever you’re trying to heat in the cooking cavity.

Conclusion
Since we’re so used to having plastic cups around, it’s only natural to try and put a cup full of tea, coffee, or any other drink into the microwave. However, before doing that, you need to make sure the cup can handle the heat generated by the oven. If it’s not designed to withstand high temps, it will quickly deform, melt, and turn into a health hazard.
Yes, most plastics need to be kept outside of the microwave to avoid exposure to chemicals. But there are a few plastic products on the market that are allowed in the cooking cavity. To check that, look at the bottom of the cup. If the label says “Microwave-safe”, that means you can use it.
Featured Image Credit: Wirestock Creators, Shutterstock
Contents