What Is a Heat Exchanger & How Does It Work? What You Need to Know
-
Pete Ortiz
- Last updated:
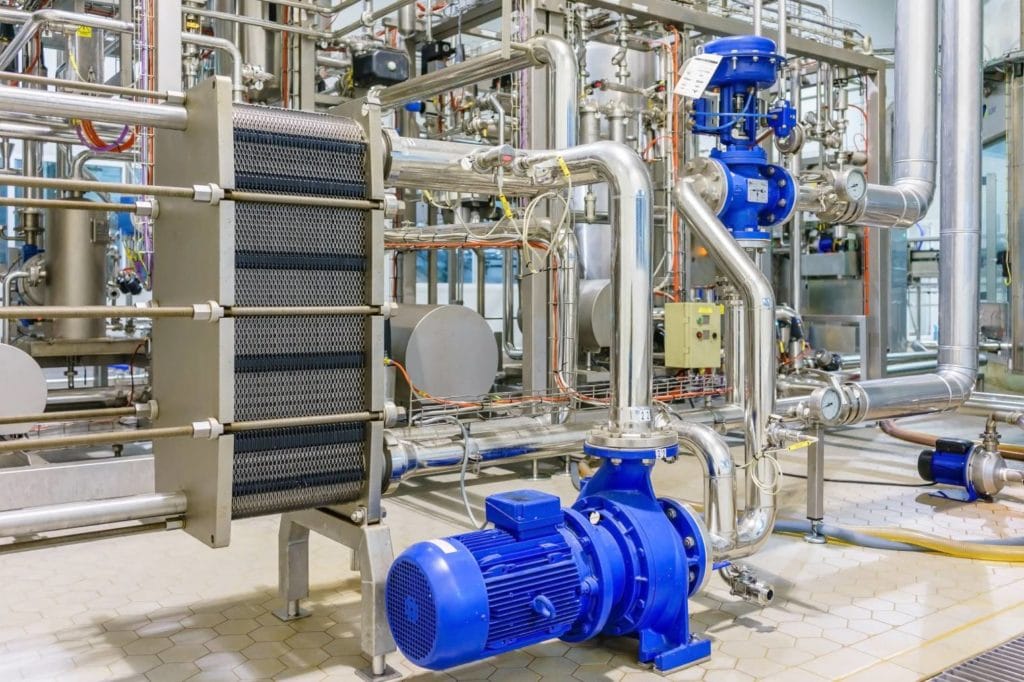

A heat exchanger is one of the largest parts of your home furnace. Its job is to safely transfer heat for many applications. It can be used for space heating, cooling, chemical plants, and even power stations. If a heat exchanger is not working properly, it can lead to many dangerous scenarios, including carbon monoxide leaks.
Because heat exchangers play a vital part in your home, you should understand the device and how it works. Unfortunately, many homeowners are none the wiser about a heat exchanger until something goes wrong and they need to get it fixed.
Below, we will learn about a heat exchanger, including what it is, how it works, and signs that it is broken. You can use this information to better understand your home and how your furnace system works. Keep reading for more.
 Heat Exchanger: What Is It?
Heat Exchanger: What Is It?
Heat exchangers are a part of your furnace. The job of the heat exchanger is to safely transfer heat from one of the furnace’s mediums to another. For a heat exchanger to do this, it must have media. Media can be a form of gas, liquid, or a combination of the two.
Because of a heat exchanger, your entire system’s energy is more efficient. The heat made from one system can be transferred to another where it is more needed. This means that the heat being produced is used for a purpose instead of just building up in your system. Let’s take an example.
In a turbine that generates electricity, waste heat is produced. This waste heat is transferred with a heat exchanger to boil water. By boiling water, a steam turbine in the system will generate even more electricity, making the system more efficient.
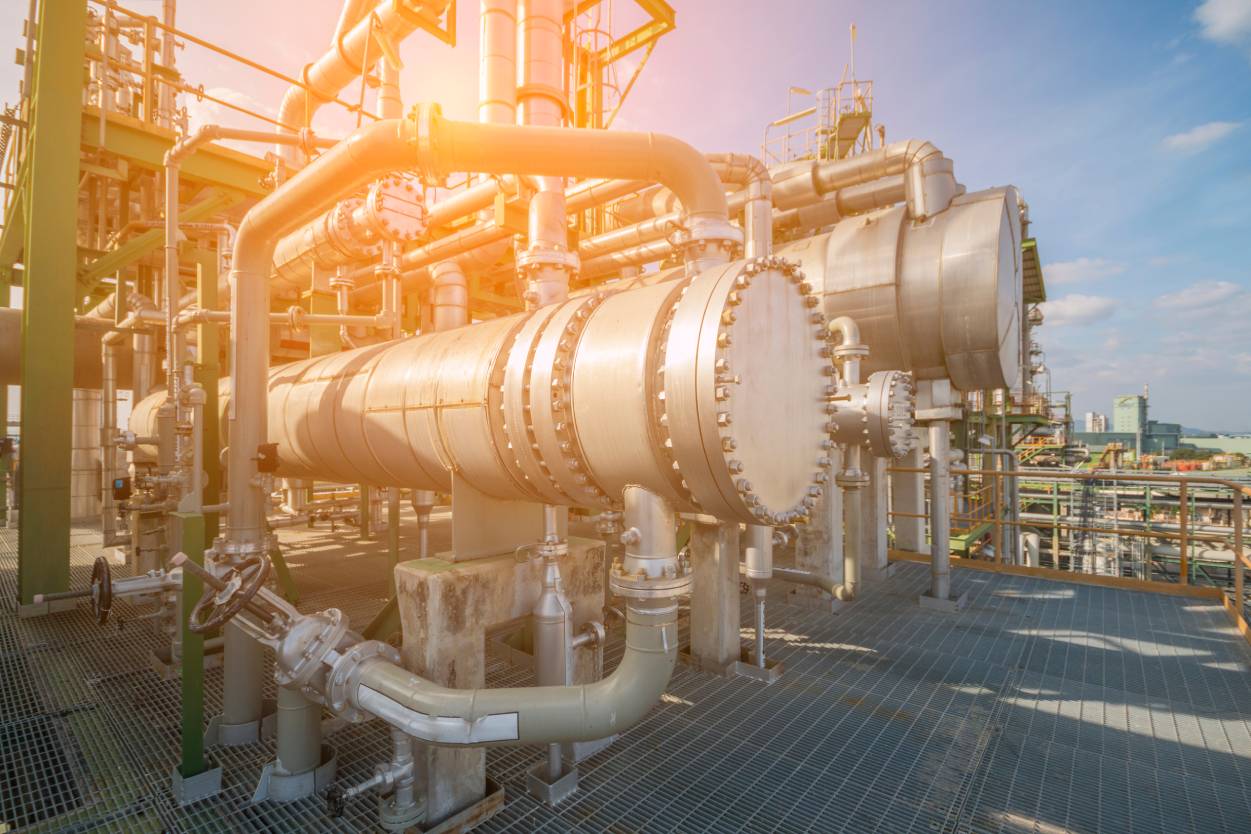

Primary vs Secondary Heat Exchanger
In many home systems, there are primary and secondary heat exchangers. The primary heat exchanger is often located closest to the furnace’s burners for increased efficiency. It will contain the hottest flue gas or media as a result.
The most efficient systems have a secondary heat exchanger too. What happens is that combustion exhaust will leave the primary heat exchanger and travel to the secondary heat exchanger instead. This allows even more heat to be released to form water vapor. The result of this is an even higher level of efficiency.
In other words, primary and secondary heat exchangers serve the same purpose, but their location is not the same. Their size is not the same either, but they work together to increase the efficiency of the system to its peak.
How Does a Heat Exchanger Work?
All heat exchangers work in similar ways. They include metal shells and tubes so that heat can be transferred from one location to the next.
For example, many systems produce hot flue gas. This gas will heat the metal as it exits out of the exhaust outlet. By heating the metal, the metal then heats the air, which circulates throughout the system so that it can be used in another way. This is just an example of a gas heat exchanger, but liquid heat exchangers work in the same way, only with liquid.

Signs Your Heat Exchanger Is Broken
When your heat exchanger is working as it should, it’s easy to forget about all the nuances of the system. Unfortunately, it can be difficult to know if your heat exchanger is broken without a physical inspection from a professional.
The most obvious sign that there’s something wrong with your gas heat exchanger is carbon monoxide problems. Flue gas used in these systems results in carbon monoxide leaking into your home if something physically wrong with the heat exchanger.
Before the heat exchanger gets to that point, you might not notice something wrong. Instead, you will have to inspect the heat exchanger directly and test for CO. Occasionally, broken heat exchangers can be detected by a visual inspection alone, but most inspections require technical tools to test the air and gases around the system.
 In Conclusion
In Conclusion
A heat exchanger is a part of your furnace that transfers excess heat to another to increase the efficiency of the furnace. Most home systems are gas-based, which can lead to carbon monoxide problems if there is an issue with the heat exchanger. Other heat exchangers have a liquid medium or liquid and gas medium mixture.
Regardless of what type of media your heat exchanger uses, it’s important to have your system inspected semi-regularly. This inspection will catch broken heat exchangers before any serious damage or health risks are done.
- See Also: How Much Does A Heat Exchanger Cost?
Featured Image Credit: NavinTar, Shutterstock
Contents

 Heat Exchanger: What Is It?
Heat Exchanger: What Is It?