Basement Mold: Types, Reasons & Prevention (With Pictures)
-

- Last updated:

Basements are especially susceptible to mold and mildew due to their location and underlying foundation. Mold refers to various fungi that commonly grow in or around homes and other building structures.
It grows under specific conditions and is known to cause allergic reactions. Mold can be hazardous depending on the type and extent of its infestation. If left untreated, basement mold can spread throughout different areas of your home, so it’s essential to identify it and treat it as soon as possible. But what are the types of basement mold?
The 5 Common Basement Mold Types
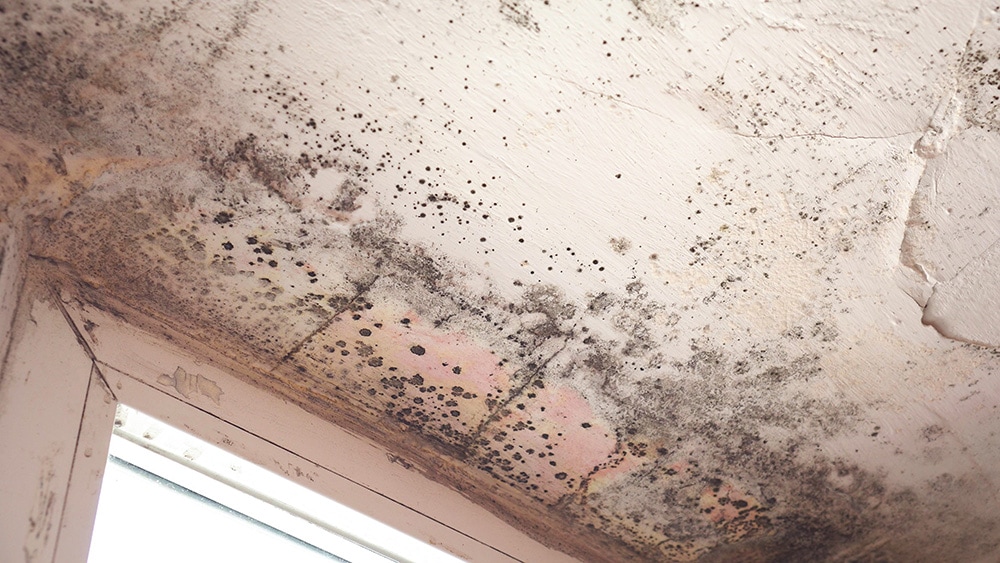
1. Black Mold (Stachybotrys)

| Fungi Class: | Sordariomycetes |
| Common Locations: | Damp places, HVAC systems |
This is the most common type of basement mold (and bathroom mold) and the easiest to identify. It’s black and appears in small or large spots on walls, ceilings, and between tile grout. There are many species of Stachybotrys. You’ll commonly see it in basements, bathrooms, sewers, and other damp and cool areas.
Stachybotrys halonata and Stachybotrys chartarum are the most common types within this species, and they’re more toxic than many others. They can sometimes be found indoors and in ventilation systems. Both species can be linked to indoor air quality problems, and they’re usually caused by excessive moisture.
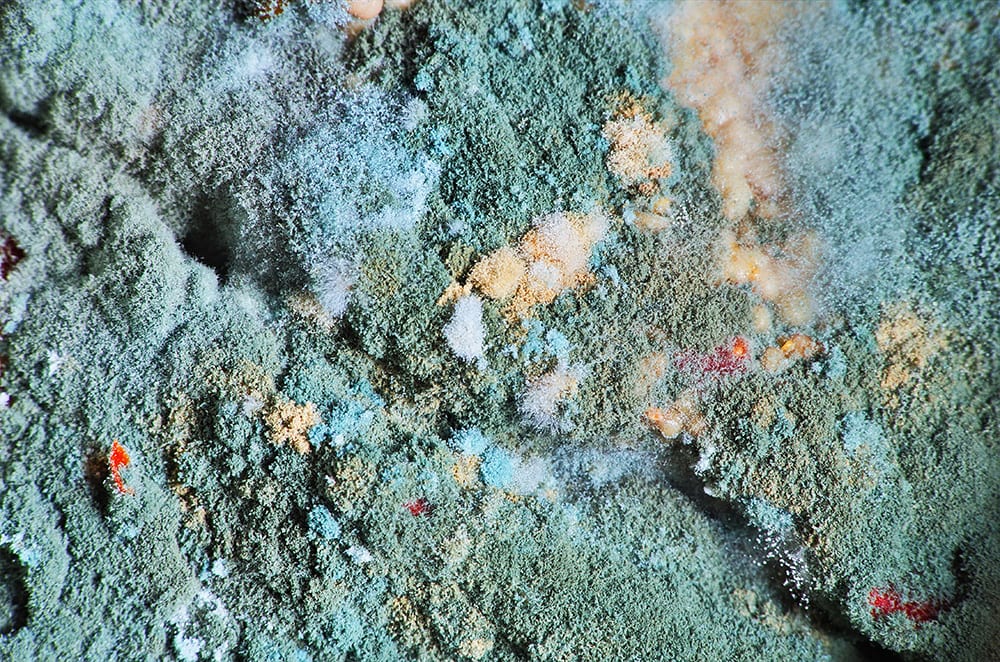
2. Aspergillus

| Fungi Class: | Eurotiomycetes |
| Common Locations: | HVAC systems, indoors, flooded areas |
There are over 100 types of molds within this fungi species. It can appear or black or bluish-green with a cloudy, almost fuzzy appearance. Although most Aspergillus is non-toxic, many species are hazardous in large numbers.
They can emit toxins in the air that trigger asthma issues and allergic reactions. Bad infestations can also cause respiratory irritation and lung infections if inhaled. Some Aspergillus species can create aflatoxins, which are compounds that can encourage cancer growth. The spores of Aspergillus fumigatus can be found in all parts of the environment and around your home’s foundation.
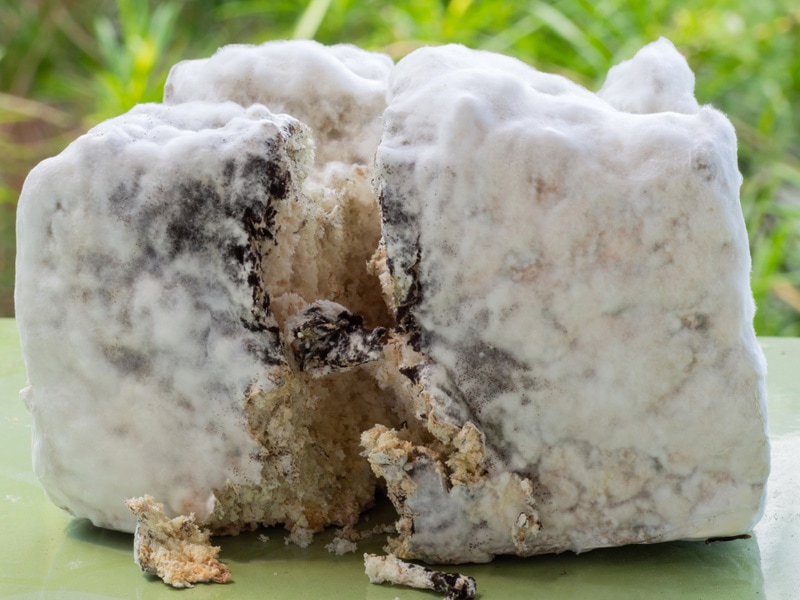
3. Penicillium

| Fungi Class: | Eurotiomycetes |
| Common Locations: | High-humidity locations in/around the home |
Penicillium is found in most natural environments and is commonly used in drug and food production. It’s also known to be the source of many antibiotics. However, it can cause allergic reactions when grown in large numbers in your basement.
It normally appears in round, fuzzy, greenish blots with white edges. It spreads quickly through the air and can cause heart or asthma-related problems. Like other molds, Penicillium thrives in high-moisture areas, which is why basements are a prime location.
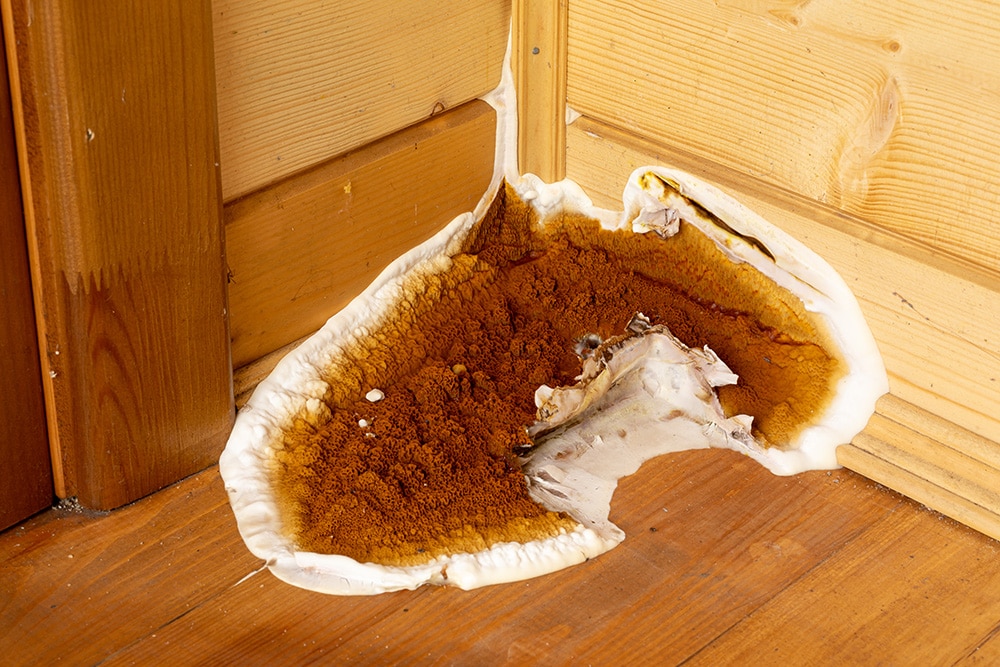
4. Serpula

| Fungi Class: | Polychaeta |
| Common Locations: | Wood-based structures |
Serpula lacrymans eat wood structures outdoors and indoors (commonly basements, attics, and crawl spaces). Although it can be irritating, it isn’t a serious health threat to humans. However, it can cause structural damage to your home if it grows in large numbers, so it’s vital to mitigate it ASAP.
It can cause dry rot and destroy beams quickly, even without substantial moisture. If you notice beams, joists, or floors with mushroom-like growths, it could signify a serpula infestation.
5. Ulocladium
| Fungi Class: | Dothideomycetes |
| Common Locations: | Damp carpets, furniture, and drywall |
Ulocladium mold can be found in moist areas such as bathtubs, showers, and window trims susceptible to condensation. It can also be found in carpets, dishwashers, and washing machines.
You can also find it along the rubber seals in your fridge or freezer, especially if the cooling system is malfunctioning. Ulocladium looks like black mold but isn’t as dangerous. However, any visible mold should be a cause for concern. Ulocladium can also be found in drywall (due to plumbing leaks) and thrives in damp environments.
 Usual Reasons for Mold in Basements
Usual Reasons for Mold in Basements
Mold spores can grow anywhere, but most require specific living conditions. Let’s take a look at the most common reasons why you may find mold growing in your basement.
Sump Pump Failure
Sump pump failure can cause mold overgrowth in a matter of days. If the pump is not maintained correctly, it can also lead to mold issues due to excess water on the floor or beneath the slab’s surface.
Water Heater Issues
When a water heater fails, it could cause stagnant water to pool, leading to damaged floors and walls. If the water heater is leaking (which commonly happens before a failure), it could lead to excess moisture and mold growth where the water has leaked.
Bad Ventilation
A lack of ventilation is one of the most common causes of basement mold. Poor ventilation causes condensation. This, in turn, causes excessive moisture in the basement, which is the perfect environment for mold to grow.

Too Many Organic Materials
This may come as a surprise, but too many organic materials in a moist basement can also exacerbate mold growth. Materials such as wood furniture, carpets, old clothes, and cardboard, combined with humidity levels of 55% or higher, can cause mold issues.
Ways to Prevent Mold in Basements
You’ll need to be vigilant to prevent mold growth in your basement. Let’s look at how you can keep your basement free from mold.
Reduce the Humidity
Mold growth thrives in moist environments. Basements can have very moist conditions even without flooding or plumbing leaks. It is crucial to control the humidity in your basement (it shouldn’t be over 55%).
A basement dehumidifier (which can be attached to your furnace) is the best way to achieve this. The dehumidifier can be set to maintain the basement’s humidity at the desired level. To make sure that humidity levels are at an acceptable level, consider purchasing a hygrometer. You can get one online for about $10.

Repair All Plumbing Leaks ASAP
Leakages can cause water pooling and wet spots, which can cause mold if left unattended for long periods. Because basements are below ground level, moisture can easily get trapped.
This commonly leads them to become very moist and mold-ridden faster than other levels of a home. You should immediately fix any leaks, dry your basement with a heater, or let it air out.
Avoid Clutter
You won’t get much airflow if your basement is cluttered with clothes, unused furniture, construction debris, trash, etc. If your basement isn’t well-ventilated, it is even more conducive to fast mold growth. This problem can typically be avoided by ensuring that clothing, boxes, and other similar items are well-organized and stored away.
Try not to keep too many loose items in your basement, especially out in the open. It’s best to leave enough space for airflow. Also, avoid placing your belongings and furniture against the wall or on the basement floor, which can block vents and normal airflow.
Conclusion
The more ventilation your basement has, the less likely it is to develop mold infestations that can lead to structural issues and potentially hazardous living conditions for you and your family. Keeping your basement mold-free means proactively reducing humidity and clutter and monitoring for water leaks.
- You Might Also Be Interested In: 10 Types of Mold in a Crawl Space
Featured Image Credit: Jezael Melgoza, Unsplash
Contents

