How Does a Generator Work? Components, Types, & Tips
-
Pete Ortiz
- Last updated:

Electricity is crucial, ideally part of day-to-day activities. We plug it into our wall sockets and fire electric coils to heat our homes. Also, we drive cars that run on electric motors and plug-in electric appliances that run on electricity.
What if there’s a power blackout? What do you use to power all these appliances? If you are one of those wondering what to use when the electricity goes out, one machine comes in handy in such situations: a generator. This is an essential piece for any homeowner. It is an energy conversion device that uses the principle of electromagnetic induction to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy.
You can use it to power computers, lights, televisions, and more. If you have ever wondered how a generator works, this guide is for you. We will discuss how a generator works, the different types of generators, and all you need to know about these handy devices. Keep reading to learn more!
How Does It Work?
Generators are a crucial component of the modern energy infrastructure. The mechanical energy comes from a spinning shaft. It spins due to an engine or other power source. As the shaft turns, it rotates wire coils within a magnetic field, creating an electric current. Then, the electric current travels through wires to provide power for your home or business.
In other words, they are devices that convert one form of energy into another. They can provide electricity in places without adequate natural gas, hydroelectricity, or coal.
When looking at how a generator works, it’s crucial to discuss its components and how each contributes to the working of the entire unit.

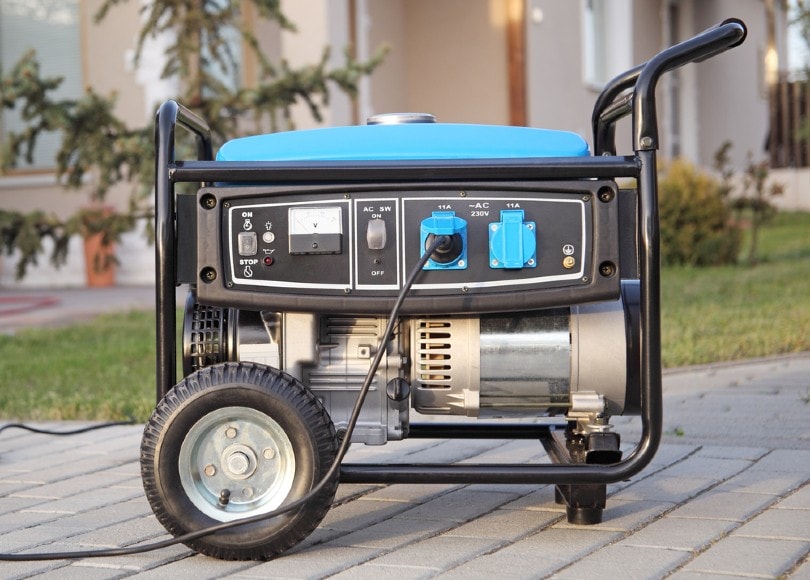
The 10 Main Components of a Generator
There are many types of generators, but their inner workings and parts are similar. A generator has several components that make it work effectively. These include:
1. Frame
The generator’s frame is the outermost part, usually made from metal. The frame keeps all other components in place and supports them as well. It also acts as an insulator for the electrical parts inside the generator. It prevents them from short-circuiting with each other or with the outside environment. The frame also allows easy handling without tampering with the inner parts.
2. Engine
The engine is the primary component of a generator system, usually located in the primary housing of a generator. It can either be an internal combustion engine or an electric motor/alternator combination. It converts mechanical energy into electrical energy through electromagnetic induction.
The maximum power output of a generator depends on the engine size. The engine can operate on various fuel types.
3. Fuel System
The fuel system consists of a tank containing liquid hydrocarbons (oil). The most common types of fuels used in generators are diesel and gasoline.
This fuel system has an electric pump that moves oil from one part of the system to another. Besides, an electronic control unit regulates pressure and flow rates. Supply and return pipes connect the fuel tank to the engine.
4. Cooling System
The cooling system is part of the engine, and its main purpose is to keep the engine cool. The heat generated from the engine must be removed so that the engine doesn’t overheat and become damaged. Most generators have a liquid cooling system. It uses oil as a coolant to transport heat away from the engine.
5. Voltage Regulator
The voltage regulator is connected directly to the terminal block on the generator. It keeps the voltage output of the generator within safe limits. It controls how much voltage is applied to the battery bank.

6. Battery Charger
When starting up, a generator depends on a battery. The battery charger ensures the battery is charged. It provides a float voltage capacity of 2.33 volts in every cell.
7. Alternator
An alternator is a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. It has coils of wire wrapped around an iron core. Alternating current flows through them.
Some alternators have an external rotor spinning inside the stator (electrical coil). Others have an internal rotor that rotates inside the stator housing. The rotor and the stator create a rotating magnetic field. They also produce an alternating current (AC) output.
8. Exhaust System
This system collects exhaust gases from an internal combustion engine, and then discharges them into the atmosphere. The exhaust system includes an exhaust pipe, muffler, and catalytic converter. It disposes of these exhaust gases via an iron or steel pipe.
9. Control Panel
The control panel consists of switches, meters, indicators, and circuit breakers. It allows you to turn the generator on and off manually or electronically. These switches also allow you to control many of the functions of your generator as well as monitor various aspects of its performance.
The control panel may include a built-in battery charger, overload protection, and safety devices. The overload protection is designed to shut down the generator when it is overloaded or overheating.
10. Lubrication System
The lubrication system keeps all the engine’s moving parts properly lubricated. The system includes an oil pump, which circulates oil throughout the engine. It also has an oil filter that removes contaminants from the oil before it circulates through the system.
In most small generators, a pressurized oil reservoir supplies pressurized oil to the engine via a hose and dipstick.
What Are the Different Types of Generators?
Generators come in all shapes and sizes, from large permanent units to smaller portable ones. They are used for various applications. You can use them to power almost anything. Also, there are different types of generators out there. So, let’s take a look at the primary types.

1. Portable Generators
Portable generators are designed to be moved from one place to another easily. Some models have wheels so they can be transported easily. Others have handles and can be carried by hand.
Portable generators are smaller than other types of generators. They are great for outdoor activities where electricity may not be available. They are also popular for homeowners who want an extra power source during emergencies or storms. They come in gas-powered, propane-powered, or electric-only models.
- They don’t need complex installation.
- They are cost-effective compared to standby generators.
- They can be moved around easily.
- They can only power essential devices in the household
- They need a manual start. So, they cannot power on automatically in case the main power goes out.
- Most portables use gas to operate and must be filled after some time.
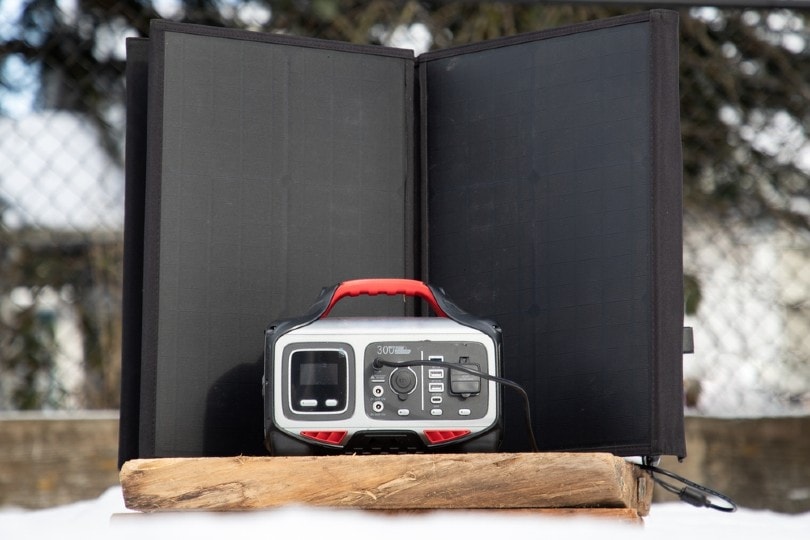
2. Inverter Generators
Inverter generators use alternative power sources such as solar panels to charge batteries within the unit. They do this before they start producing electricity through an inverter circuit board. The inverter circuit board is similar to those found in home appliances, such as microwave ovens or televisions.
These types of generators are more expensive than standard generators. They’re also quieter and more efficient. They convert DC into AC power instead of using a mechanical motor like other types of generators do. It means they don’t produce as much heat or noise when operating. It makes them ideal for use at home or even in your RV.
Inverter generators are dissimilar to other generators because they use a rectifier when converting DC to AC power. An inverter generator can adjust the engine’s speed to only what’s needed.
- Fuel-efficient
- Produces low noise
- Generates clean power
- Needs minimal maintenance
- More expensive than portable generators
- Have a low power output
3. Standby Generators
Usually, standby generators are installed outside a home or business to produce electricity when there is a power outage or in an emergency. They have automatic start capabilities, so they will turn on automatically during an outage. You can use them as backup power sources during blackouts caused by severe weather.
Standby generators are typically used for commercial purposes where there is an immediate need for power generated from a constant source. These generators provide consistent power with minimal disruptions during blackouts.
These units need little maintenance. They don’t run continuously like portable models, so there is less wear and tear and less risk of fire hazards due to overheating parts inside the unit.
- Dependable
- They can operate for a long time
- They switch on automatically
- They’re not noisy
- Standby generator installation takes time
- They’re more costly compared to other generators
Where are Generators Used?
A generator is a handy appliance in many fields and situations. Some of them include:
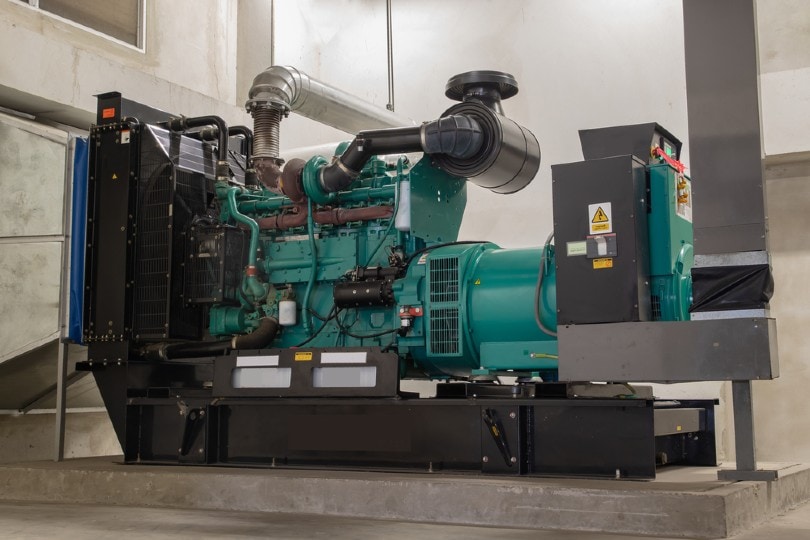
Routine Power Outages
You can use your generator to provide power when the grid goes down due to an outage or harsh weather. If you’re in a location that experiences routine power outages, it may be worth investing in a portable generator just for this purpose.
It will keep your electronics, lights, and other crucial devices running while waiting for power to come back.
Emergencies
If natural disasters strike your area, you may need to rely on a portable generator for energy. Outages often occur after severe weather events, such as hurricanes and tornadoes. So, having a generator ready could be critical in these situations.
Standby Power
Generators provide standby power for businesses, hospitals, and schools during a power outage. Critical facilities can continue operating without interruption while the utility company repairs the damage.
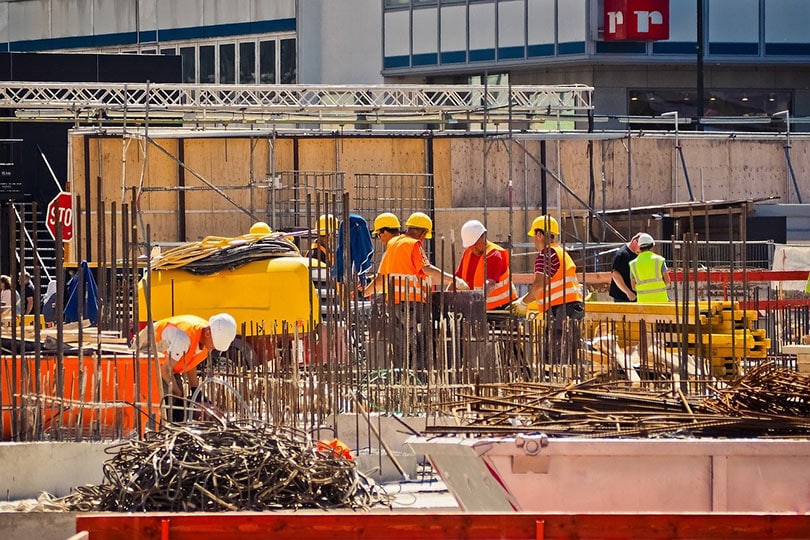
Construction
Construction sites often have generators to provide electricity for their tools, light towers, and other equipment that need power. These generators must be sturdy enough to stand up to the elements and run for many hours. They must also produce enough electricity for all the construction equipment.

Camping
If you love spending time outdoors camping or hiking, a portable generator or an inverter generator is perfect to power your tent and other camping gear while you’re out in nature. You can also use it to charge phones and other devices. The best generator to use in this case is an inverter generator since it is quiet.
Mining
Mining sites often need a lot of power for mining machinery, similar to construction sites. They don’t have access to a power grid. A generator can produce electricity. With this, miners can use their equipment without interruption.
Weddings and Family Reunions
Family reunions and weddings are a time of celebration for everyone. That includes lighting up the celebration venue with beautiful lights. In the absence of electricity, the event may come to a standstill. But you can use the generator to power up lamps or even music systems.
Fairs and Carnivals
A carnival or fair is an event where people gather to have fun. They have different features like rides, food stalls, games, and more. Generators provide power for various appliances in these events, including bounce houses and cotton candy machines.
A Quick Reference Guide
| When to Use a Portable Generator | When to Use an Inverter Generator | When to Use a Standby Generator |
| When powering a refrigerator | When charging a car battery | In emergency settings |
| Powering nail guns | When charging a laptop battery | When there’s a power outage in a hospital |
| When you want to power spray gun systems | N/A | N/A |
Tips for Maintaining Your Generator
Keeping your generator in good condition is not only a great idea, but it’s also essential. There may be some differences in how you maintain it depending on the type, but the same basic principles apply.
Here are some tips to help you maintain your generator:
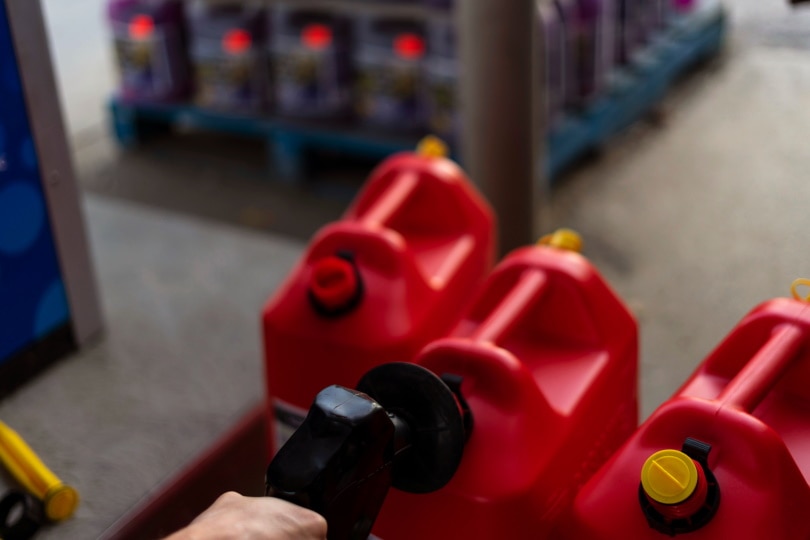
Change the Oil
Changing the oil is a crucial thing you need to do when taking care of your generator. Change the oil at least once every 100 hours of usage or after every 2 years, whichever comes first.
If you fail to do so, there is a possibility your generator will break down due to insufficient lubrication or overheating.

Ensure the Generator is Clean
The generator should be clean at all times. If there is dust or dirt accumulation, clean it off before they get onto any other parts.
The components of a generator, such as a stator and a rotor, attract dirt and dust, so they need regular cleaning. Also, if your generator runs in dusty conditions, clean it often. Ensure you remove dust and debris from the air filters.
Inspect the Generator Once a Month
Inspecting the generator will help you avoid costly repairs down the road. You can identify potential problems before they become severe. Start the generator once a month even if you’re not using it. You don’t want to find out your generator isn’t running when you need it.
Storage
If you want to store your generator, drain the tank and ensure the fuel lines are empty. Then, store it in a dry area without any debris. Also, ensure it’s a cool place away from direct sunlight.
FAQs
1. When are you supposed to replace your generator?
The lifespan of a generator depends on the number of hours it has been running. The longer it’s been running, the more likely it is that something may go wrong. The average lifespan for a properly maintained generator is around 30 years.
However, if you use your generator more often, you may need to replace it sooner compared to the one being used once or twice a year.
2. What safety precautions should you observe when using a generator?
Never use a generator indoors. Generators produce carbon monoxide (CO) gas. Carbon monoxide kills quietly and can be fatal even in small quantities. So, don’t run your generator inside your home or garage.
Also, operate the generator in a dry place. Avoid using it in rainy conditions. Generators come with instructions on how to operate them. Read them carefully before attempting to start your generator.
3. What can make your generator unstable?
Damaged parts in the generator system will make your generator unstable. Another reason for the instability is inadequate cooling systems or overheating of the engine.
Besides, if your generator is not maintained well, it’ll not last as long or run as efficiently as it should. If the oil levels are too low or there’s dirt in the engine, this will cause damage over time and make the machine less stable.
•You might also like:Does Homeowners Insurance Cover Electrical Panel Replacement?
Conclusion
Generators allow us to generate electricity to meet the demands of our homes and businesses. We have given a deeper insight into how generators work and broken it further into the various components. We have also looked at the types of generators and where they can be used.
Whether you are holding an event or fear power outages in your area, with a generator, you are well covered. Regardless of what you use a generator for, you will be well covered in case of emergencies, power outages, and in areas where there is no power access.
Now that you know how a generator works, why not buy one for your home? They can prove surprisingly beneficial in an emergency or disaster situation.
- Components of a Generator
- How Does a Generator Work?
- What are the Different Types of Generators?
- Advantages and disadvantages of Portable Generators
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Inverter Generators
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Standby Generators
- Where is a Generator Used?
- Tips for Maintaining your Generator to Last Long
- When are you supposed to replace your Generator?
- What should you not do with Generators?
- What can make your Generator Unstable?
- WBDG
- SPORTS N’ HOBBIES
- INNOVATIVE ELECTRICAL CONTRACTING INC
- ELECTRICAL SAFETY
Featured Image Credit: canoniroff, Shutterstock
Contents


