18 Types of Coconuts (With Pictures)
-

- Last updated:

There are about 18 common varieties of coconuts around the world. All these coconuts belong to the Arecaceae family, otherwise known as the palm tree family. Coconut trees belong to the genus Coco, and they are the only living species that belong to this genus.
Coconut trees are typically separated into one of two categories: dwarf trees and tall trees. These categories describe the height of the trees. From there, there are many varieties that are separated based on the fruit, leaves, and other parts of the plant.
The 18 Types of Coconuts
1. King Coconut

| Tree Type: | Dwarf |
| Characteristics: | Perfect oval; extra sweet flavor |
The King Coconut is an important fruit in Sri Lanka. Both the flesh and water are sweet and packed full of nutritional value. These trees are short and available throughout the entire year. Just after 8 months, the fruits are ready to harvest.
2. Green Dwarf Coconut
| Tree Type: | Dwarf |
| Characteristics: | Stays green; more water than flesh |
Although many coconut varieties can have green hues, the Green Dwarf Coconut has a distinctive green color. Even when ripe, this coconut stays green. This variety is primarily grown in Malaysia, and it has more water but less flesh than other varieties.
3. Fiji Dwarf
| Tree Type: | Dwarf |
| Characteristics: | Durable; special leaf structure |
The Fiji Dwarf is a popular variety among gardeners because it is durable and resistant to a lot of diseases. The plant itself is also very beautiful and produces delicious fruit. The special leaf structure of this tree further makes it popular among gardeners.
4. Chowghat Orange Dwarf Coconut
| Tree Type: | Dwarf |
| Characteristics: | Large; sweet meat |
The Chowghat Orange Dwarf Coconut is a unique species. The fruit is super large, and the coconuts have a bright orange color. This species best grows in India where it will produce a lot of fruit that has plenty of meat and sweet water inside.
5. Malayan Yellow Dwarf Coconut
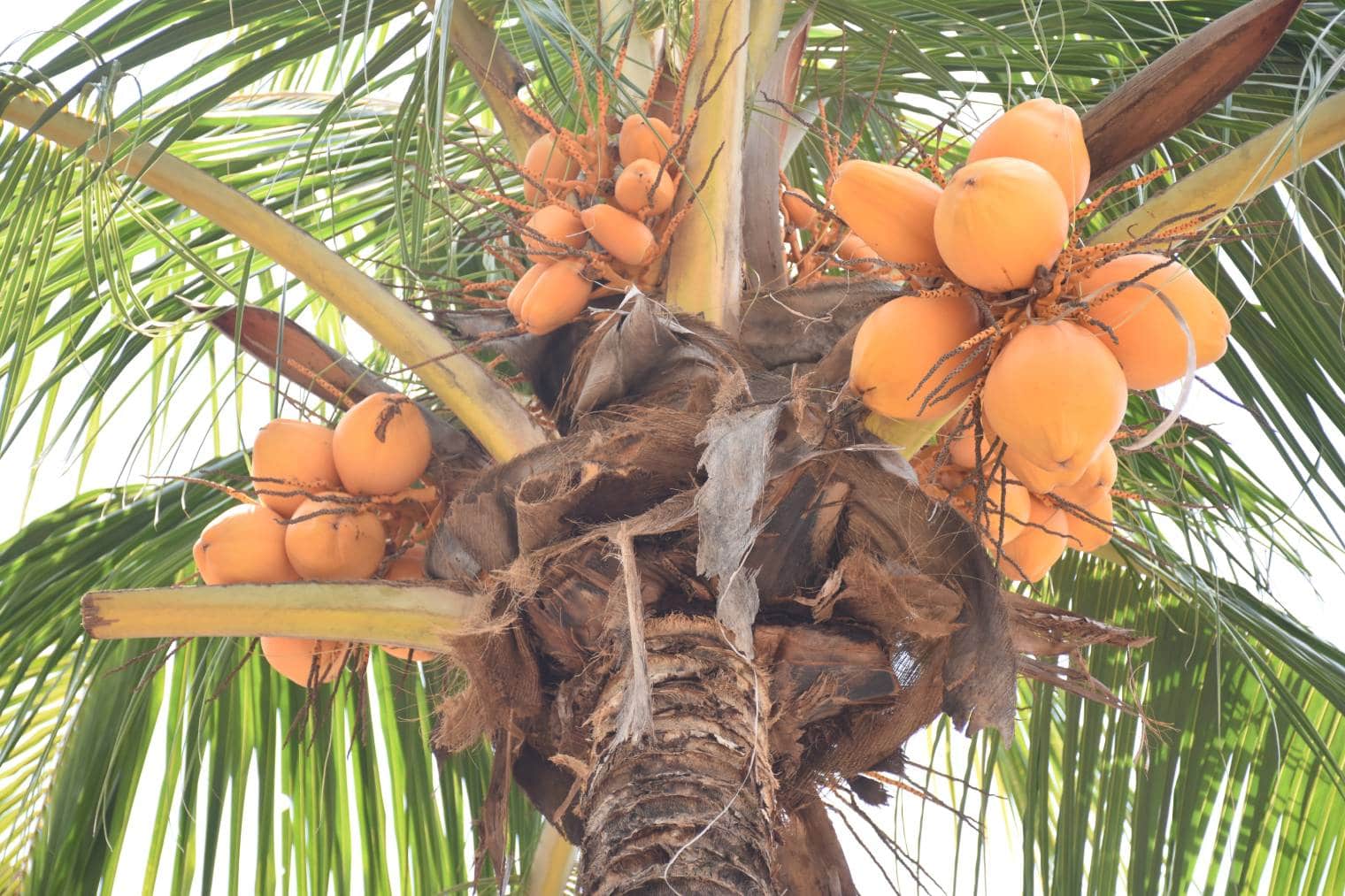

| Tree Type: | Dwarf |
| Characteristics: | Pale yellow; easy to grow |
The Malayan Yellow Dwarf Coconut originated from Malaysia during the 1800s, but these coconuts are now grown in Brazil, Fiji, India, Jamaica, and Thailand. As you might suspect from their name, this coconut is known for its light yellow to green shade, but they are mainly pale yellow once fully grown.
6. Golden Malayan Dwarf Coconut
| Tree Type: | Dwarf |
| Characteristics: | Golden-orange; high water content |
The Golden Malayan Dwarf Coconut is similar to the coconut mentioned above, but it has a different coloration. The coconut is golden orange, making it a beautiful coconut to look at. For a dwarf species, this coconut can grow tall and reach 60 feet. It is best grown in warm conditions.
7. VHC1 Coconut
| Tree Type: | Dwarf |
| Characteristics: | High coconut yield |
The VHC1 Coconut is a hybrid between the Malayan Green Dwarf that we have looked at and the East Coast Tall Coconut that we will look at shortly. This combination allows this species to produce more coconuts than most other dwarf species.
8. Panama Tall Coconut
| Tree Type: | Tall |
| Characteristics: | Durable; highly sweet |
The first tall species we are going to look at is the Panama Tall Coconut. This species is highly resistant and able to withstand harsh temperatures. This Tall Coconut does not produce a lot of fruit, though.
9. Jamaican Tall Coconut
| Tree Type: | Tall |
| Characteristics: | Highly productive; sweet fruit and water |
The Jamaican Tall Coconut tree is super productive and can create 200 coconuts a year. These trees are super tall and can grow to be 100 feet and live to be 80 years old. Although this coconut originates from the country of Jamaica, it is found all around Florida and Latin America.
10. East Coast Tall Coconut
| Tree Type: | Tall |
| Characteristics: | Green; pest resistant |
The East Coast Tall Coconut produces a lot of water, and they are resistant to pests. This variety is popular for making coconut oil because about 64% of the flesh is coconut oil specifically.
11. West Coast Tall Coconut
| Tree Type: | Tall |
| Characteristics: | Easy to grow; high oil content |
Despite its name, West Coast Tall Coconuts can be grown everywhere. Their fruit produces a lot of water that is great for cooking. The meat inside also has a lot of oil, making it a popular tree for coconut oil production.
12. Maypan Coconut
| Tree Type: | Tall |
| Characteristics: | Resistant; durable in harsh weather |
The Maypan Coconut is a hybrid between the Malayan Dwarf and the Panama Tall. This coconut tree is loved because it is resistant to a lot of diseases and is great for rough weather. Despite being a tall species, this tree is actually more medium-sized.
13. Macapuno Coconut
| Tree Type: | Tall |
| Characteristics: | Almost no water; jelly-like texture |
The Macapuno Coconut was developed in the 1930s. This species is known for its dry fruit. The inside of the coconut is filled with a lot of meat, but there is practically no water at all. The texture of the meat is a bit different and replicates the texture of Jelly.
14. Kera Sankara
| Tree Type: | Tall |
| Characteristics: | High oil content |
The Kera Sankara is a hybrid between the Chowghat Orange Dwarf and Lakshadweep. This variety produces a lot of oil. Its oil content is between 68%–72%.
15. Tiptur Tall Coconut
| Tree Type: | Tall |
| Characteristics: | Not durable or resistant |
The Tiptur Tall Coconut is one of the most classic varieties. It has a standard amount of water to meat ratio. The only downside of this species is that it is not disease resistant and it does not withstand rough weather very well.
16. Chandrakala Coconut

| Tree Type: | Tall |
| Characteristics: | Fast producing; easy to grow |
The Chandrakala Coconut produces about 100 nuts per year, and it produces a whole lot of water. Unfortunately, it is difficult to extract the water, which means its water is mainly only extracted for commercial purposes.
17. Chandra Laksha
| Tree Type: | Tall |
| Characteristics: | High oil content; fast producing |
The Chandra Laksha is a fast-producing variety that is a mixture between the West Coast Tall and the Chowghat Orange Dwarf. It has a high oil content of 68%.
18. Lakshaganga
| Tree Type: | Tall |
| Characteristics: | Durable; high oil content |
Finally, the last coconut on our list is the Lakshaganga. It is a cross between the Green Dwarf and the Lakshadweep. It does not produce a lot of fruit until it reaches maturity. Then, it produces about 100 coconuts a year with about 70% oil content.

Where Are Coconuts Originally From?
As you learned above, coconuts are grown all around the world. Where exactly did they originate? Studies have found that there are actually two origins of cultivation.
The first is in the Pacific where coconuts were cultivated in Southeast Asia. Indonesia, Malaysia, and the Philippines are most likely where the Pacific coconuts were mostly harvested before spreading.
The second is in the Indian Ocean. Experts believe that the center of cultivation was around southern India, including the Laccadives, the Maldives, and Sri Lanka.
What Are the Benefits of Coconuts?
Coconuts are a beloved fruit because they come with numerous benefits. The fruit itself provides tasty meat and water that is delicious for recipes but healthy at the same time. Coconut provides a lot of healthy fiber, minerals, and nutrients, all while tasting sweet.
Conclusion
Now that we have looked at 18 types of coconut, it’s time for you to start trying them all so you can pick out your favorite. More than likely, you’ll find all varieties to be delicious, healthy, and a sweet treat.
Featured Image: Daniel Dan, Pexels
Contents

