Where Does a Washer Go? Types, Uses & FAQ
-
Pete Ortiz
- Last updated:
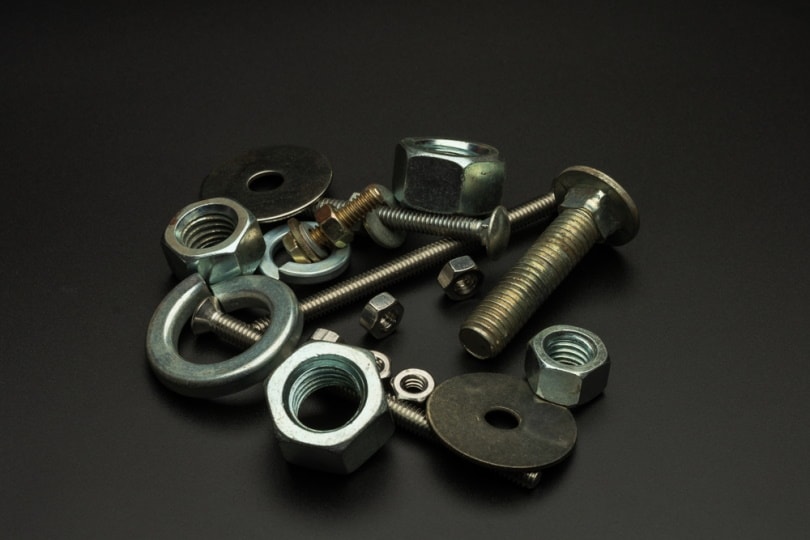

Various types of washers are available, and the type you use depends on how it should be fitted, whether it should go on the nut or bolt side, and whether you should use a washer on each side. The purpose of all washers is to prolong the life of the fastener and prevent damage to the object underneath.
In general, where only one washer is used, it will go on the nut side because it is the side that twists and is more likely to suffer damage. However, there are occasions when the washer should be placed on the bolt side. You can keep reading for more information on washers, including the various types and their ideal placement.
Types of Washers
Various types of washers offer protection against damage.
- Flat Washers – The most common type of washer, the flat washer or plain washer, is a circular disc with a smaller hole cut out of the middle. It is a single piece of metal designed to be used as a space to separate two surfaces. They primarily distribute the force applied when the fastener is tightened. This prevents the nut or other fasteners from drilling into the surface, which not only causes damage to the surface but allows for a more secure fastening. Although flat washers are commonly made from metal, they can be made from other materials, including plastic.
- Lock Washers – Lock washers cut into the fastening surface. This allows for greater friction between the fastener head and the surface and gives a better and more secure grip than a flat washer. Different lock washers are available, with one of the most common being the serrated lock washer.
- Shoulder Washers – Shoulder washers look like flat washers but have a bushing that insulates the fastener. They protect against electricity and are typically made from a non-conductive material like nylon. They are not typically used for domestic purposes but are commonly found in electrical and electronic applications.
- Spring Washers – A spring washer serves the same purpose to prevent damage to the surface and ensure a tight grip between the fastener and the surface, but it is specifically used to prevent movements caused by vibration. The spring washer is similarly designed to a flat washer, except that it is cut, and the sharp edge of the cut washer digs into the fastening surface and provides an improved grip.
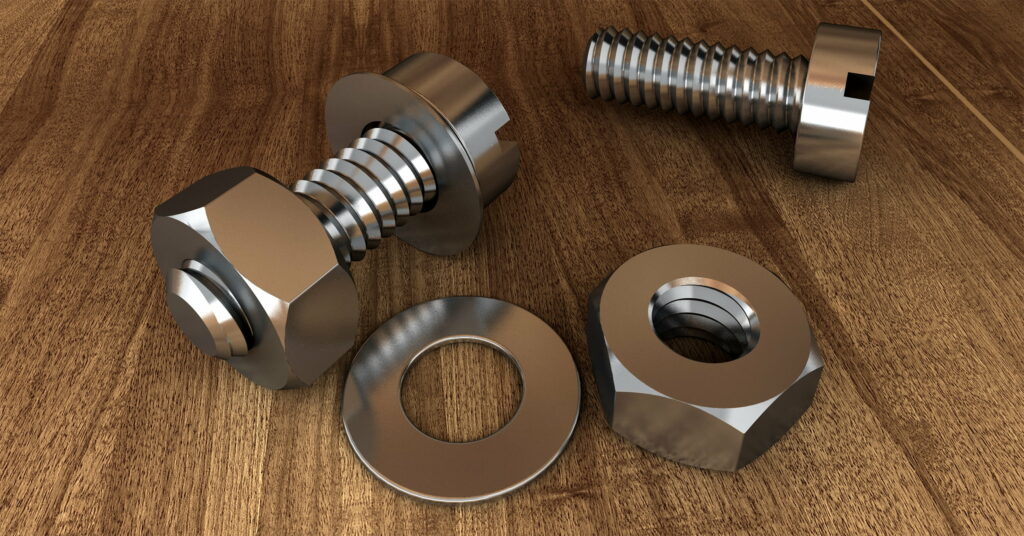
Uses for Washers
Different types of washers serve various purposes, with the main functions including:
- Surface Protection – Washers more evenly divide the load from the fastener as it is screwed, which means less pressure is placed on a smaller area of the fastening surface. This prevents the fastener from digging into, splintering, or cracking the surface. Washers are required for this purpose where the fastening material is softer than the fastener; otherwise, a washer is not usually needed.
- Spacing – A washer can work as a spacer where a bolt or other fastener is slightly too long for the purpose it is being used. This may require the use of two or more washers to ensure that the gap is fully closed.
- Protection Against Vibration – Vibrations can be very damaging to certain surfaces, and vibration-dampening washers, usually made of a material like rubber, negate the vibrations and prevent any damage they would cause. In this case, the washer will be placed on the side where the vibrations are strongest, whether that be the nut or bolt side.
- Protection Against Liquid – Liquid sealing washers can prevent liquid from passing through the fastener and the surface ingress, therefore preventing leaks. These washers tend to be made of silicone and are most commonly used in water pipes and water systems.
Which Side Does a Washer Go On?
The side where the washer will be placed depends on its purpose. Where it’s being used to protect a surface, it’s placed against the nut or the bolt, whichever one will be turning. In most cases, this is the nut side. Alternatively, they can be placed on the side that will endure the most vibrations, and where two washers are available, they can be placed on both sides to ensure proper protection.
Which Way Does a Washer Go?
Generally, washers have a flat side and a curved side, and the flat side will be placed against the fastening surface.
Do You Always Need to Use a Washer?
It isn’t always necessary to use a washer; in some cases, a washer will have very little or no effect. This is especially true when the fastening surface is as hard or harder than the fastener and when there is no need for insulative or liquid protection. Generally, it is best to use one where a washer is advised or provided.

Should You Use Washers With Screws?
Washers can be used with almost any fastener fastened against a surface. This includes screws, and when screwing into wood, using a washer can help to give a solid and secure fastening.
Conclusion
Washers are typically used to spread the load applied to a surface when a fastener like a nut and a bolt is tightened to the surface. The washer helps protect that surface by spreading the load and acting as a physical barrier. The washer usually sits on the nut side, but one can be used on each side, and it is sometimes beneficial to have the washer on the bolt side.
Featured Image Credit: Georges_Creations, Shutterstock
Contents


