Cinder Block vs. Concrete Block: What’s the Difference?
-

- Last updated:
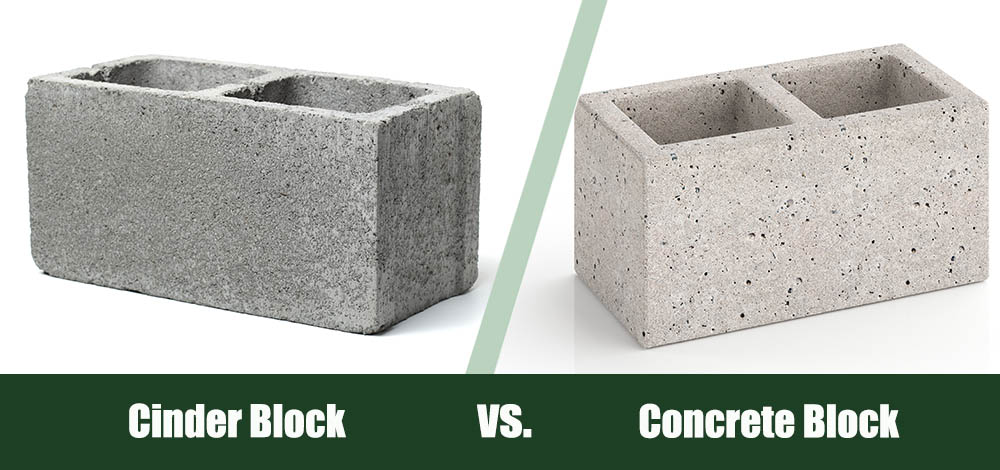
Home construction requires proper planning and suitable materials. When building, there are two types of blocks you can use: cinder and concrete blocks. Both are durable masonry blocks that come in various sizes and shapes and are easy to work with. However, each has its unique properties that tell it apart.
Familiarizing yourself with these two types of blocks is an excellent way to narrow down your decision. You’ll also know what qualities to look out for and which ones to avoid. We’ll discuss each block type in this handy guide, focusing on several primary differences between them. Keep reading!

Overview of Cinder Block
Cinder blocks are made from concrete and coal cinders (byproducts of coal combustion). They’re similar to concrete blocks except that their aggregate filling material is coal cinder.
They have excellent insulating properties, and they help reduce noise transmission. They are mostly used for building houses, walls, and other structures. They are also helpful for interior partitions as they provide support without increasing the load.

Properties of Cinder Blocks
- Structural Properties: Cinder blocks have a higher compressive strength than other masonry units such as natural stone. However, they have low tensile strength and poor resistance to impact. You must reinforce cinder block walls with steel rebar or wire mesh because they are not load-bearing.
- Fire Resistance: Although cinder blocks are not fire-rated, they are known to be fire resistant to some extent as they are made from concrete. But again, they’re not completely fireproof. They may not burn down if exposed to fire or extreme heat but may crumble and collapse if it gets too hot or if there is repeated fire exposure.
- Water Resistance: Cinder blocks are not highly water resistant. If they are exposed to standing water or excessive moisture, they will begin to degrade and lose their structural integrity.
- Insulating Properties: Insulating properties are measured in R-value (thermal resistance). A higher R-value means better insulation properties. Cinder blocks have a low R-value. Given their poor insulating properties, they need extra material to boost their R-value.
- Aesthetic Properties: Cinder blocks are an excellent choice for building the exterior of your home, especially if you want to create an old-world look. These blocks come in various textures and colors, and you can paint them to match any color scheme. Besides, you can use them with other materials such as brick, stone, or wood to create a unique look without breaking the bank.
- Acoustic Properties: Cinder blocks have excellent acoustic properties. They can absorb sound waves and vibrations because of the small voids between them that act as acoustic insulation and reduce noise pollution. The blocks are also heavy enough to act like a noise barrier.
- Lightweight
- Less number of joints due to its large size
- Stronger than bricks
- Insulates against noise, dampness, and heat
- No plastering needed
- It saves you cash as it requires less mortar
- Fewer skills needed to install
- Inexpensive
- Cannot endure tension and pressure
- Requires a lot of repairs and maintenance
- May not be suitable for various locations
- Produces weak foundations
Overview of Concrete Block
Concrete blocks are one of the most common materials used in various construction projects such as building walls, foundations, and even for landscaping. They are sometimes called CMU (Concrete Masonry Units).
A concrete block is a precast product, meaning it is formed and hardened before being taken to the construction site. The blocks are made from cement mixed with sand, gravel, or other aggregates. The mixture is poured into molds that form the shape of the block. Once the concrete sets, it’s compressed and then bonded together to create a solid block of material resistant to cracking and water damage.
As already mentioned, concrete blocks are especially good for building foundations and giving a solid base for your home, garage, or shed. Let’s look at several properties of concrete blocks.

Properties of Concrete Blocks
- Structural Properties: The strength of a concrete block is higher than any other building material, and it doesn’t crack easily. They can support heavy loads without needing extra reinforcement.
- Fire Resistance: Concrete blocks contain cement, which has a high melting point. They can withstand high temperatures without losing their strength or shape. It makes them ideal for use in areas prone to high temperatures, such as fireplaces and chimneys. The blocks are not entirely fireproof, but they are fire-resistant.
- Water Resistance: Concrete blocks have a high percentage of cement, which makes them highly water resistant. If you live in an area prone to floods, you are better off with concrete blocks as they do not hold water due to their porous nature. Also being dense, they absorb little moisture through their surface.
- Insulating Properties: The concrete blocks’ density determines their insulating properties. The blocks have a porous structure with tiny pores and cracks that allow air to flow through them. This reduces heat loss. Their high R-value makes them excellent at stopping heat transfer, thus keeping the heat in during the winter and out during the summer.
- Aesthetic Properties: The appearance of concrete blocks varies depending on the type you choose. Some are more attractive than others, with some having smooth surfaces and others having rougher textures. Some types also come in different colors. Concrete block makers are producing new concrete block sizes and shape to suit the ever-growing market.
- Acoustic Properties: Concrete blocks are manufactured from high-quality concrete, which has excellent acoustic properties. Their sound absorbency makes them ideal for soundproofing walls and rooms in homes and offices. They’re also perfect for constructing auditoriums, schools, and hospitals. The sound absorption capacity depends on the thickness of the concrete block.
- Increase acoustic performance
- High thermal insulation
- Low maintenance costs
- Highly durable and resistant to adverse weather conditions
- Fire-resistant
- Excellent thermal insulation
- The large size reduces construction time
- They may be prone to water seepage over time
- Usually not attractive
- Can be costly
- Must be dry before installation
Differences Between Cinder and Concrete Blocks
You’re probably looking for the best material to build your walls but don’t have much experience deciding the best material. That’s when it helps to differentiate between cinder and concrete blocks.
Weight
Concrete blocks are heavier than cinder blocks because they comprise sand and stone. Cinder blocks are much lighter and, thus easier to transport and handle. They also take less time to install since they don’t need much force when lifting them.
The lighter weight of cinder blocks is helpful when carrying them around, but it can be a disadvantage if you want to build a wall to withstand heavy loads.

Lifespan
Cinder blocks have a lifespan of up to 80 years. On the flip side, concrete blocks can last up to 100 years. The difference in longevity depends on the quality of construction and materials used. Cinder blocks are not as strong as concrete blocks and may crack or crumble if not well-built.
Cost
The initial cost of cinder blocks is less than that of concrete blocks. This is because they are made of cinders, which can be easily manufactured.
Concrete blocks have a higher initial cost. Manufacturing them requires more cement, sand, and gravel. The processes involved in making them are also more complex than those used to make cinder blocks.
Maintenance
Though the initial cost of concrete blocks is higher, they’re cheaper as they need minimal maintenance. On the other hand, cinder blocks cost less but require more maintenance which makes the costs add up quickly.
Strength
Concrete blocks are stronger than cinder blocks because they have cement as an ingredient that makes them harden faster and increases their tensile strength. On the other hand, cinder blocks aren’t strong enough to endure high pressure.
Fly Ash
Cinder blocks are made from fly ash, a byproduct of coal-fired power plants. Fly ash is a fine powder used as an additive in concrete mixtures. It reduces the amount of cement needed in the mix. Ash is helpful in the construction of wall units in concrete blocks. This means that in cinder blocks, ash is an ingredient, but it’s not an ingredient in concrete blocks.

Cinder Block vs. Concrete Block: Which One Is Right for You?
Concrete blocks are your best bet if you’re looking for building blocks that will last for years with minimal maintenance. But if the initial cost is an issue and you don’t mind doing some upkeep now and then, cinder blocks may be a better option for you. But remember, their maintenance cost is higher than concrete block
Concrete blocks are strong. You can use them to construct any structure. Cinder blocks are outdated construction elements only ideal for small construction projects.
- For a lightweight construction project, such as garden walls
- If you want to make a birdhouse, grill, or firewood storage
- To decorate
- If you want a safety barrier
- For heavy and large construction projects
- If you want walls to protect you from the elements.
- If you want to support heavy loads against the wall
Conclusion
Both cinder and concrete blocks are designed with the same purpose and function in mind. But they each offer their unique advantages and disadvantages. Depending on your needs and lifestyle, one may be better than the other for some situations.
Your project may be a large or a small one. If you have the right building supplies, excellent craftsmanship, and an eye for detail, your cinder or concrete blocks will work to complement your project’s design.
- https://dreamcivil.com/cinder-block/
- https://dreamcivil.com/cinder-block/
- https://www.hunker.com/12310270/properties-of-concrete-blocks
- https://civilquery.com/what-is-concrete-block/
- https://civiljungle.com/cinder-block-vs-concrete-block/
- https://dailycivil.com/difference-between-cinder-blocks-concrete-blocks/
- https://www.e-education.psu.edu/egee102/node/2062
- https://www.cement.org/cement-concrete/products/concrete-masonry-units
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32324165/
Featured Image Credit: (L) zhengchengbao, Shutterstock | (R) Kutcenko, Shutterstock
Contents