8 Facts and Statistics About Insulation to Know in 2025
-
Ed Malaker
- Last updated:

Note: This article’s statistics come from third-party sources and do not represent the opinions of this website.
You can find insulation in any home in America. It’s also in many other related structures, such as the garage, shed, and more, yet very few people know much about it. If you need to install it, you can find the large number of brands available confusing if you don’t know what you need. If this sounds like your situation, keep reading while we go over several facts and statistics about insulation to help you learn more about it and get the information that you need to purchase and install it in your home.
Click below to jump ahead:
Top 8 Insulation Facts and Statistics
- Insulation slows heat transfer but does not block airflow.
- You must seal drafts before you add any insulation.
- The R-value tells you how efficient the insulation is.
- Insulation does not stop working.
- Insulation saves the most energy.
- Insulation is recyclable.
- Insulation reduces carbon dioxide by 780 million tons each year.
- An uninsulated home can lose up to 60% of its energy through the walls.

Insulation Facts
1. Insulation slows heat transfer but does not block airflow.
(Griffith Energy Services)
Many inexperienced homeowners mistakenly believe that adding insulation will help block drafts and reduce airflow throughout their homes. Unfortunately, this is not the case, as scientists designed insulation to slow heat transfer, causing it to act similarly to a thermos that keeps your coffee hot. It prevents energy from being lost through the walls, so your furnace won’t need to turn on as often to keep your house warm. It also helps keep the house cool when using the air conditioner in the summer.
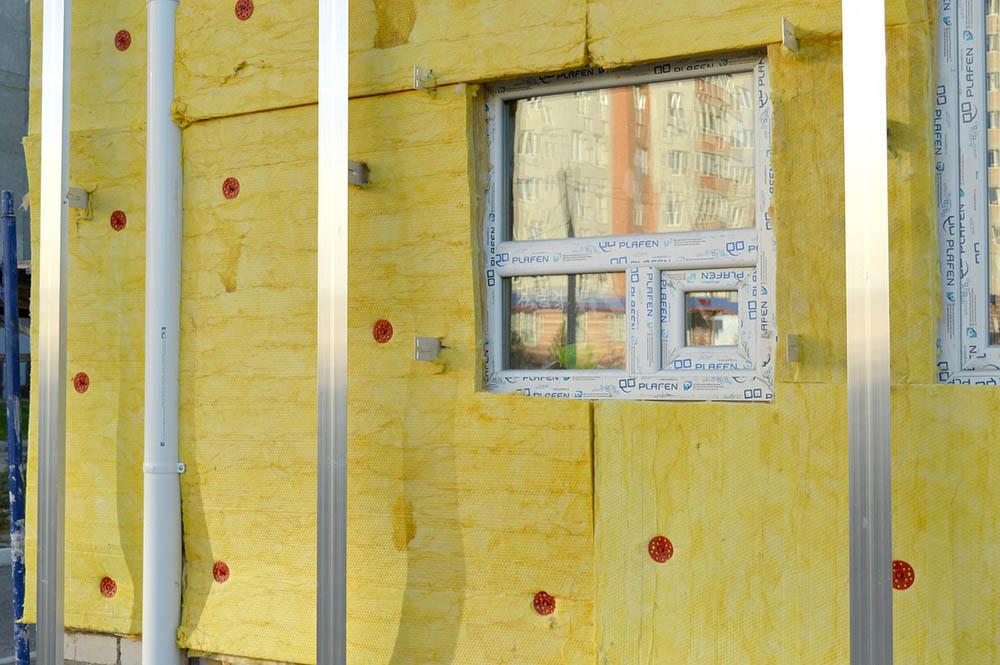

2. You must seal drafts before you add any insulation.
(Griffith Energy Services)
It’s important to go through your home carefully, sealing up any drafts before adding insulation. You can use several products, including caulking, weather stripping, and expanding foam, to seal up any gaps in your walls and around your windows to prevent unwanted airflow. It’s important to do this before you add the insulation because the insulation will not prevent airflow. Once you install it, you may have difficulty finding any holes causing a draft. You will also need to remove the insulation to get at it, increasing your workload.
3. The R-value tells you how efficient the insulation is.
(Griffith Energy Services)
Many inexperienced first-time insulation buyers are more concerned with the type of insulation or how much they need to purchase, and they forget to look at the R-value, which tells them how efficient the insulation is. Another thing that can make this value more confusing is that if you take two pieces of insulation made of the same material but with a different thickness, the thicker insulation will have a higher R-value. This fact confuses many people into thinking that the R-value is related to thickness when it isn’t. Simply put, the higher the R-value, the less insulation that you will need.
4. Insulation does not stop working.
(Insulate Kansas City)
Unlike many other things that wear out over time and stop working as effectively as they did when they were first purchased, insulation is not affected by time and will continue to work the same way as long as it is sealed away from the environment where wind, sunlight, and moisture might break it down. You may find your insulation settles over time and you need to add more, but you will never need to completely remove and replace it.

5. Insulation saves the most energy.
(Insulate Kansas City)
Many people spend plenty of money on energy-saving devices like furnaces, portable heaters, LED lighting, and more, but these only conserve how much power they use. Although higher energy star ratings use less power, insulation doesn’t require any power at all, and yet it saves more energy than all these devices combined.
6. Insulation is recyclable.
(Insulate Kansas City)
While fiberglass is not recyclable, cellulose is and is itself a recycled material. You might also consider insulation recyclable because if you no longer need it in one house, you can remove it and put it in another. This fact is true for both fiberglass and cellulose.
Insulation Statistics
7. Insulation reduces carbon dioxide by 780 million tons each year.
(Insulate Kansas City)
Since insulation reduces the amount of heat that escapes through your walls, your furnace needs to do less work. Less runtime means your furnace will consume fewer fossil fuels, which can help save on energy costs and reduce carbon dioxide emissions, helping improve the environment. Experts suggest that insulation currently in place across the United States helps reduce carbon dioxide emissions by 780 million tons each year.
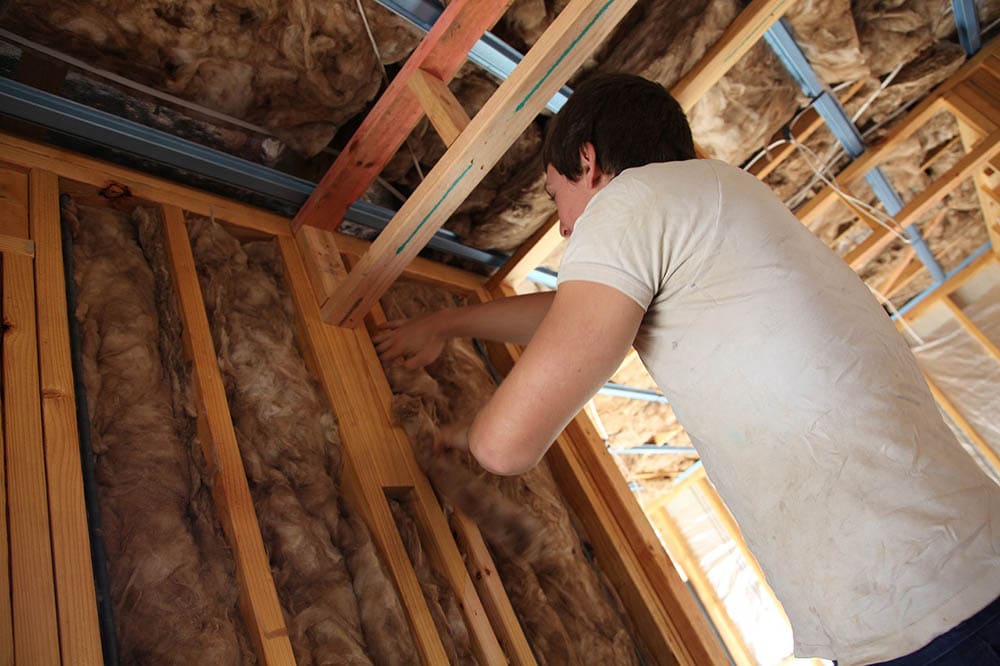

8. An uninsulated home can lose up to 60% of its energy through the walls.
(Oliver Heating and Cooling)
Experts suggest that your home can lose up to 60% of its energy through the walls if there is no insulation. This energy loss can dramatically increase your heating bills and carbon dioxide emissions. It will also be difficult to remain comfortable in cold or hot weather because you won’t be able to fully control the temperature in your home
Frequently Asked Questions About Insulation
What types of insulation are there?
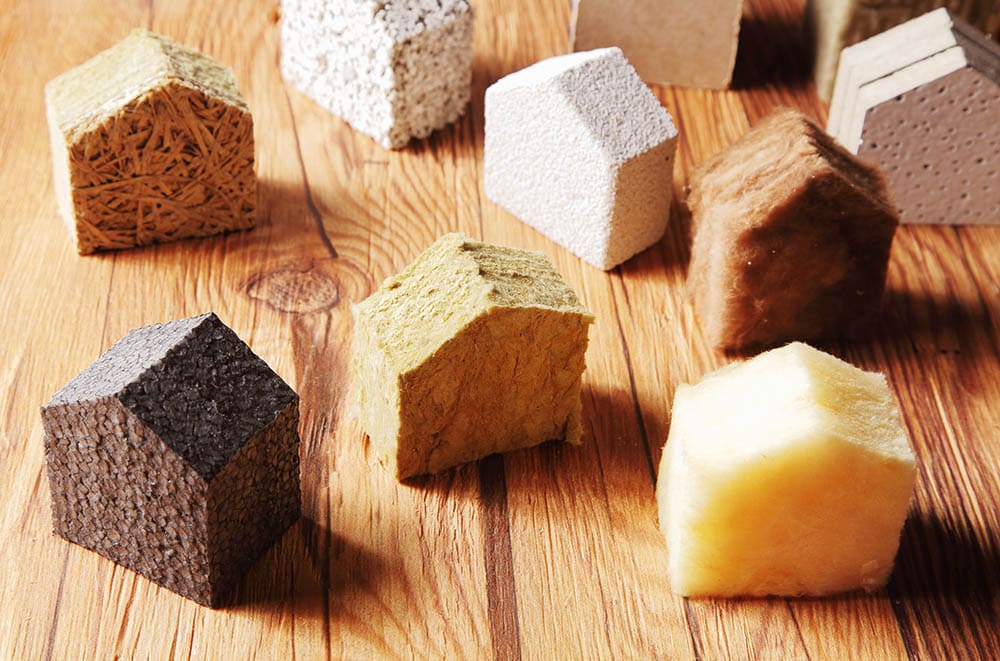
There are several types of insulation, but the most popular are cellulose and fiberglass. You often find fiberglass in large rolls or end sheets that make it easy to install. Cellulose is recycled paper that you blow into the wall to create a thermal barrier. Other popular types of insulation include spray foam and mineral wool, which come in large rolls or batts like fiberglass and provide additional fire resistance. You may also find insulation made from natural fibers like sheep’s wool, cotton, and hemp. There is even insulation made from recycled denim.
What kind of insulation should I use in my home?
The kind of insulation that you will need to use in your home will depend on where you’re putting it and the R-value that you need.
Loose fill
Loose-fill insulation is best for attics, places where there already is insulation, and hard-to-reach places where it would be difficult to unroll or nail sheets of insulation.
Insulation batts
Insulation batts are best for walls and ceilings because they are easy to nail in place and have a protective paper backing that makes them easier to handle.
Rolled insulation
Rolled insulation is similar to insulation batts, but there’s no paper backing, and it will typically contain much more insulation than a single insulation batt. So, it’s perfect for covering a large area with tight-fitting insulation.
Foam board insulation
Foam board insulation is a type of rigid insulation, so it’s well suited for floors, walls, and sloped ceilings. It’s easy to cut and nail into place, and it has a high R-value.
Spray foam insulation
Spray foam insulation can be quite messy because it’s sticky and tends to get all over you when you try to apply it. However, it’s perfect for filling small gaps around doors, windows, and vents, and it’s ideal for hard-to-reach and oddly shaped areas.
How do I know what R-value I should use?
The Department of Energy recommends R-values depending on your climate zone. The numbers range from 1 to 7, and the colder the climate, the higher the number. The Department of Energy lists suggested values for each part of your home, so there is no confusion. When you purchase your insulation, you will look at the R-value to know how much to use. For instance, suppose that you live in zone 3, which calls for an R-value of 30–60 in the attic. You should purchase insulation with an R-value of 5 per inch. You will need to layer the insulation until it is 6 inches deep to reach an R-value of 30 and put down an additional 6 inches to reach an R-value of 60. Besides the attic, the Department of Energy also provides recommendations for walls, frames, and more. (Energy.gov)
•You might also like:How and When to Prune Cherry Trees – What You Need To Know!
Conclusion
Installing insulation can be a great deal of work if you are inexperienced and have many hard-to-reach places and tight corners. However, installing it in an attic or basement can be simple and only requires you to unroll it or nail it in the right place. When working with insulation, it’s important to wear a mask and gloves, especially when using fiberglass. When you’re consulting the Department of Energy for your R-rating, if you get two values, we recommend going for the higher value if you can afford it because it will save you money in the long run with reduced energy costs.
See also: What Is Insulation Made Of? 5 Common Materials
Featured Image Credit: stockcreations, Shutterstock
Contents