Do Teslas Have Engines? Facts & FAQ
-
Pete Ortiz
- Last updated:

Tesla quickly made a name for itself upon launching the all-electric Roadster in 2008, displaying the brand’s vision of vehicular evolution. Teslas have no internal combustion engine (ICE). Instead, they rely on electric motors to independently power axles or individual wheels.
A quiet, eco-friendly ride may be the most obvious benefit of any Tesla EV, but electric cars offer performance perks that are hard to match in a gas-powered vehicle. Let’s explore what makes these vehicles so intriguing by diving a little more into the engine design.
What’s Under a Tesla’s Hood?
Pop the hood of any Tesla vehicle, and you’ll see nothing but a lined cavity underneath. The “frunk” offers extra storage to supplement the trunk in the back.
The added space is a premium feature you won’t find on your everyday gas-powered vehicle. Some models from high-end brands like Porsche, Lamborghini, and McLaren also offer front storage space. But the traditional motor array is still limiting. Lacking the enormous internal combustion engine, Teslas can offer far more space than more expensive options.
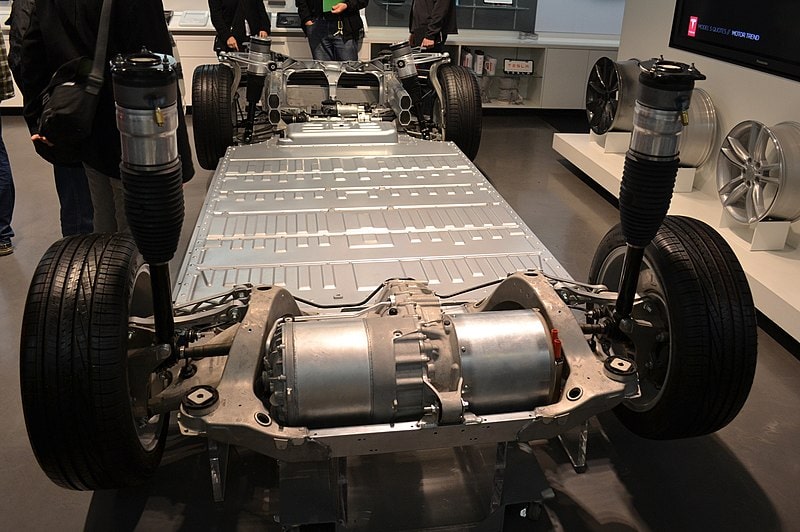
How Does the Tesla Motor Work?
Tesla does not use an internal combustion engine or any typical powertrain components. There is no transmission or drivetrain to the separate axles. EVs instead rely on an induction motor powered by rechargeable batteries to directly power axles or wheels.
Tesla models vary in the number of motors they use. Rear-wheel drive Teslas have a single electric motor connected to the rear axle, while dual-motors use a front axle motor and a rear axle motor. Tri-motor versions, as in the Model S Plaid and Model X Plaid, have three motors, one for each rear wheel and one for the front axle.
Taking the gas engine, transmission, driveshaft, and other mechanical pieces out of the equation means that Tesla’s electric motor offers a vastly superior power-to-weight ratio. It does this thanks to its infinite torque, capable of running from 0–18,000 RPMs.
Without the full range of rotational speeds, the electric motor would have the same limitations as an ICE.
You can’t attach an ICE directly to the axle because it has a narrow RPM range, often around 1,000–6,000 RPMs. It needs several gear configurations in a transmission to translate these limited RPMs into a broader range of speeds, say 0–120 mph. That’s why you’ll come closer to redlining while accelerating before dropping RPMs as the transmission shifts up a gear.
Since Tesla’s motors don’t require these gear changes, the power can attach directly to the wheels, cutting weight and providing seamless acceleration. The only bridge is a small, single-speed transmission from the motor to the axle.

Induction Motors
Tesla’s standard motor design is an induction motor consisting of two parts, a rotor housed in a stator. DC power from thousands of battery cells goes to an inverter. The inverter changes the power to AC and regulates the voltage and frequency of the current going to the motor, acting as the system’s brain.
The stationary stator is a cylindrical shaft that takes the three-phase AC input from the inverter. As it receives the input, it creates a rotating magnetic field (RMF) with four magnetic poles (two north, two south).
The rotor is a cylindrical shaft inside the stator composed of several parallel conducting bars. The RMF from the powered stator imposes electromagnetic forces on the rotor’s bars and induces a current. As the current interacts with the RMF, it puts force on the rotor and causes it to spin.
The beautiful part of this design is that the RMF’s speed relates to the AC power input. As you change speed, you signal the inverter to vary its frequency, causing the RMF and rotor to spin faster or slower within its 0–18,000 RPM range.

Permanent Magnet
Induction motor rotors lag behind the RMF in an asynchronous motion and have no permanent magnets. The magnetism in the rotor’s bars is only present when the RMF induces a current.
In Tesla’s internal permanent magnet-synchronous reluctance motor (IPM-SynRM), the rotor replaces the bars with permanent magnets. With permanent magnets, the rotor can follow the RMF in a synchronized fashion through magnetic and reluctance forces.
Unlike conducting bars in induction motors, permanent magnet rotors don’t draw power from the RMF to produce their magnetism. As a result, IPM-SynRMs are more efficient and can generate more torque. They provide constant torque through a broader speed range, giving better performance in different driving situations.
How Many Motors Do Tesla Vehicles Use?
IPM-SynRM designs are more expensive than induction motors, so Tesla hasn’t completely replaced them in their vehicles. The IPM-SynRM debuted in the Tesla Model 3 and is quickly becoming standard on more models.
The dual-motor Model 3 and Model Y use induction motors in the front axles with an IPM-SynRM in the rear. Dual-motor Model S and Model X vehicles also have a mixed pairing but put the permanent magnets up front instead and the induction motors in the back.

High-performance models such as the Model S Plaid and Model X Plaid use only IPM-SynRMs in their tri-motor design. The carbon-wrapped PM rotors can reach up to 20,000 RPM.
The upgraded motors for Tesla’s rear wheels and front axle provide maximum torque. That’s why the Model S Plaid can speed from 0 to 60 mph in under two seconds. The independent rear wheel motors also offer torque vectoring to improve stability and traction control.
Conclusion
Teslas don’t have traditional engines, giving you several benefits beyond a low carbon footprint. The instant torque, single-speed transmission, and low weight get you off the line faster than most gas vehicles while providing smooth, whisper-quiet acceleration.
Tesla continues to innovate in its battery and motor designs. Vehicles are faster, more versatile, and longer-running. As the prospect of a quad-motor Cybertruck looms, Tesla fans are champing at the bit to see how the latest evolution will again change the game.
Featured Image Credit: Piqsels
Contents


